A few readers/commenters of my blog brought attention to a video of Warren Mosler where he claims that “there is no such thing as a capital flight” – presumably for a nation with a “sovereign currency” with the implication that a Euro Area nations can simply leave the Euro and adopt their original currency without a fear of capital flight post the event.
(Why have capital controls then, if that’s the case?)
Link @22:15
This claim can be easily dismissed by simple balance of payments analysis.
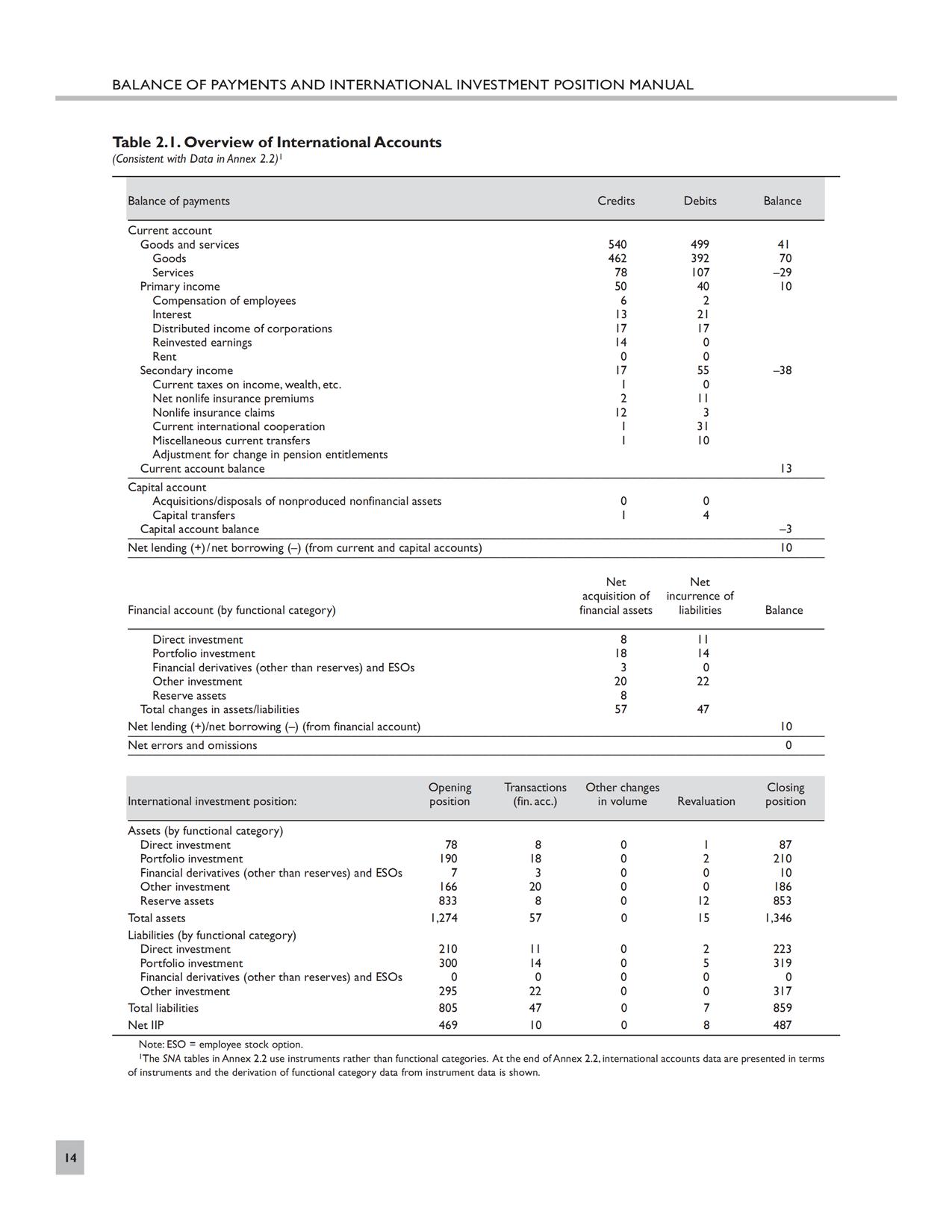
For this I use the IMF’s Balance of Payments Manual (BPM6). First lets look at the format of the BPM6’s numerical example.
The example is below:
(click to enlarge)
Roughly Mosler’s argument is that if a foreigner sells assets denominated in the domestic currency, some other foreigner would need to buy it.
He gives a Bretton-Woods anti-analogy where – presumably – an official foreign creditor can demand gold for conversion and repatriate it home by ship. And that since official convertibility to gold is suspended, there is no capital flight according to this mini-story.
To see there is capital flight, one needs to look at the foreign exchange market microstructure. By the way, the Neochartalists erroneously tend to treat banks as brokers (as opposed to dealers) in the foreign exchange markets. Let us say a foreigner – perhaps a financial institution – with “portfolio investment” in the country in question liquidates assets in the domestic currency and exchanges it at a domestic bank (domestic with respect to the country we are discussing). This “order flow” leaves the bank with a short position in foreign currency which it will try to eliminate. This will lead to a cascading effect because the foreign dealer it may want to offload its position will react itself and hence a series of transactions in the fx markets – leading to a depreciation of the currency.
It may happen that the currency depreciation may bring in an order flow in the opposite direction – thereby leading to a quasi-equilibrium. However if the general expectations is such that the currency may depreciate further then it is hard. If such expectations are formed, there may be even more capital ouflow!
It is precisely here that the central bank may intervene and sell foreign reserves – thereby helping the dealers (both domestic and foreign to offload their undesired positions). So recently there was news of intervention by the Reserve Bank of India in the fx markets. (minor technicality: the reduction of domestic banks’ settlement balances due to the settlement of central bank fx sales will lead to a “fine tuning reverse operation” by the central bank)
So how does the whole thing look in the balance of payments? The answer is very simple: assuming foreigners sold 100 units of assets – minus 100 due to liquidation of domestic assets and minus 100 due to sale of reserve assets.
So that’s capital flight.
And … like that … it’s gone!